Hiring employees in Argentina presents significant opportunities for businesses seeking to expand operations in South America. The country offers a highly educated, skilled workforce operating under comprehensive labor protections. To hire legally in Argentina, businesses must comply with the Labor Contract Law (Ley de Contrato de Trabajo) and register with relevant government authorities including AFIP (Federal Administration of Public Revenue) and the Ministry of Labor. This guide outlines the key advantages and requirements for hiring in Argentina in 2026.
Why Hire in Argentina?
Argentina has emerged as one of Latin America’s most compelling destinations for international hiring, particularly for companies in technology, professional services, and knowledge-based industries. The country combines a strong educational foundation with a culture of innovation, producing thousands of highly qualified professionals annually who are eager to work with global companies.
Beyond talent availability, Argentina offers practical advantages that matter to businesses: competitive operational costs, seamless time zone alignment with North American markets, and a workforce that’s both technically proficient and culturally aligned with Western business practices. Government initiatives actively support international hiring through tax incentives and workforce development programs, making Argentina not just an opportunistic choice but a strategically supported one.
Whether you’re looking to build a remote development team, establish a customer service center, or hire specialized professionals, Argentina provides the infrastructure, talent, and business environment to succeed. Here’s what makes Argentina stand out:
Skilled Talent Pool
- Argentina produces over 30,000 STEM graduates annually from prestigious institutions including the University of Buenos Aires (UBA), National Technological University (UTN), and Argentine Catholic University (UCA)
- The country excels particularly in software engineering and development, ranking among Latin America’s top tech talent markets
- Strong capabilities in data science and analytics
- High concentration of bilingual professionals with widespread English proficiency in professional sectors
- Robust creative and design industries with strong traditions in advertising, UX/UI, and digital media
- Argentine professionals typically demonstrate strong understanding of local labor regulations and business practices, making onboarding and compliance smoother for international employers
Cost Advantages
- Salary competitiveness: Depending on role and seniority, salaries in Argentina can be 40–70% lower than comparable positions in the United States, while maintaining high quality of work
- Lower infrastructure and office space expenses compared to developed markets
- Competitive benefits packages relative to North American and European standards
- Favorable tax structures for certain sectors under government incentive programs
- Tax considerations: Argentina operates a progressive income tax system where employers must withhold taxes from employee salaries according to AFIP regulations
- Proper worker classification (employee vs. contractor) is essential to ensure correct tax withholding and avoid penalties, fines, or legal liability
Time Zone Alignment
- Argentina operates on Argentina Time (ART), UTC-3, with no daylight saving time as of 2026
- 3-hour difference with U.S. Eastern Time, providing overlapping work hours from 9 AM–5 PM EST
- 4-hour difference with U.S. Central Time
- Excellent synchronization for real-time collaboration with North American teams
- Reasonable overlap with European business hours (4–5 hours ahead of GMT)
Remote Work Infrastructure
- Major cities (Buenos Aires, Córdoba, Rosario, Mendoza) offer reliable high-speed internet connectivity
- Well-established coworking spaces and tech hubs throughout urban centers
- Strong remote work culture, particularly in technology, marketing, and creative sectors
- Growing freelance economy with professionals experienced in international collaboration
- High digital literacy across the professional workforce
Cultural Compatibility
- Communication style: Direct yet relationship-focused, similar to U.S. and European business norms
- High English proficiency: Particularly strong in business, technology, and customer service roles
- Education system: Western-influenced curricula and business methodologies
- Work ethic: Professional, deadline-oriented, and quality-focused approach
- Business practices align closely with North American and European expectations
Government Support and Incentives
- Knowledge Economy Law (Ley de Economía del Conocimiento): Provides tax reductions and incentives for technology and knowledge-based companies in software development, biotechnology, professional services, and audiovisual production
- Argentina Programa: Government-backed initiative investing in technology education and upskilling, focusing on programming, software development, and digital skills
- Target of 70,000+ new tech professionals by 2030 through government training programs
- Innovation support: The Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation provides grants, subsidies, and financial backing for tech startups and R&D initiatives
Key Compliance Considerations for 2026
- Register as an employer with AFIP and obtain a tax identification number (CUIT)
- Comply with mandatory benefits including aguinaldo (13th-month salary), vacation time, and severance provisions
- Understand termination regulations and associated costs under Argentine labor law
- Properly classify workers to ensure correct tax withholding and labor protections
- Consider partnering with an Employer of Record (EOR) or establishing a legal entity for full compliance with local regulations
Key Statistics on Hiring in Argentina (2026)
| Statistic | Details |
|---|---|
| Official Language | Spanish (notably high English proficiency in tech and business sectors) |
| Time Zone | Argentina Time (ART), UTC-3 (no daylight saving time as of 2026) |
| Currency | Argentine Peso (ARS) |
| Exchange Rate | Approximately 1,458 ARS per USD (as of January 2026) |
| Population | Approximately 46 million |
| Internet Penetration | 90.6% (41.6 million internet users) |
| Labor Force | Approximately 22.3 million |
| STEM Graduates | Approximately 30,000 annually |
| Major Talent Hubs | Buenos Aires, Córdoba, Rosario, Mendoza |
| Minimum Wage (January 2026) | ARS 341,000/month (approximately USD $234) |
| Remote Work Preparedness | High—a digitally-savvy workforce with robust infrastructure in urban areas and strong culture of freelance and remote work |
Note on minimum wage: The Argentine government has set a progressive schedule for minimum wage increases throughout 2026, starting at ARS 341,000 in January and reaching ARS 376,600 by August 2026. The USD equivalent fluctuates based on exchange rates, which have been volatile in recent months.
Top In-Demand Roles in Argentina
Argentina’s labor market includes a wide range of skilled professionals, with particular strength in technology, digital services, and business operations. Below are the most sought-after roles by international employers:
Software Development
- Front-end Developers (React, Angular, Vue)
- Back-end Developers (Node.js, Python, Java, Ruby)
- Full-stack Developers
- Mobile App Developers (iOS, Android)
- DevOps Engineers
- QA Engineers and Testers
- AI and Machine Learning Engineers
- Blockchain Developers
The demand for software development roles has surged, driven by Argentina’s growing tech ecosystem and startup culture. Companies are increasingly seeking developers with expertise in cutting-edge technologies like AI, machine learning, and blockchain to stay competitive. The country’s strong educational background and bilingual capabilities make Argentinian developers highly attractive to global firms. Employers must also consider the responsibilities involved in hiring and managing Argentinian employees, including payroll setup, compliance with local tax laws, and legal requirements for background checks.
Sales & Marketing
- Sales Development Representatives (SDRs)
- Account Executives
- Digital Marketing Specialists
- SEO/SEM Experts
- Social Media Managers
- Content Creators (copywriting, video editing)
As businesses expand their digital presence, the need for skilled sales and marketing professionals has never been greater. Argentina’s workforce offers a blend of creativity and analytical skills, essential for roles in digital marketing and content creation. The country’s alignment with Western business practices also ensures seamless integration with international teams.
Professional Services
- Accountants and Bookkeepers
- Financial Analysts
- HR Specialists and Recruiters
- Administrative Assistants
- Project Managers
Argentina’s professional services sector is robust, with a strong emphasis on financial analysis and human resources. The country’s professionals are well-versed in global business standards, making them ideal for international companies looking to optimize their operations and manage cross-border teams effectively.
Customer Support & Operations
- Customer Service Representatives
- Technical Support Agents
- Virtual Assistants
- Operations Coordinators
- BPO Specialists
The rise of remote work and digital transformation has increased the demand for customer support and operations roles. Argentina’s high English proficiency and cultural compatibility with Western countries make its workforce ideal for these positions. Companies benefit from cost-effective solutions while maintaining high-quality service standards.
Overall, Argentina’s diverse talent pool and strategic advantages make it a prime location for hiring in-demand roles across various industries. By tapping into this market, businesses can leverage skilled professionals to drive innovation and growth.
Monthly Salary Ranges in Argentina (USD)
The monthly salary ranges in Argentina vary depending on the industry, job position, and level of experience. On average, the monthly salary ranges in Argentina are as follows:
- Entry-level positions: $400-$700 USD per month
- Mid-level positions: $700-$1,200 USD per month
- Senior-level positions: $1,200-$2,500 USD per month
- Executive-level positions: $2,500-$5,000 USD per month
It’s worth noting that these salary ranges are approximate and can vary depending on the specific company, industry, and location.
Paying Workers in Argentina
Paying workers in Argentina requires compliance with the country’s labor laws and tax regulations. Employers must pay employees in Argentina on time and in full, and must also make the necessary payroll deductions, including social security contributions and income tax. The payment process typically involves setting up a local bank account and registering with the relevant authorities. Employers must also comply with the minimum wage requirements, which are set by the government, and provide employees with the necessary benefits, including paid sick leave, maternity leave, and annual leave.
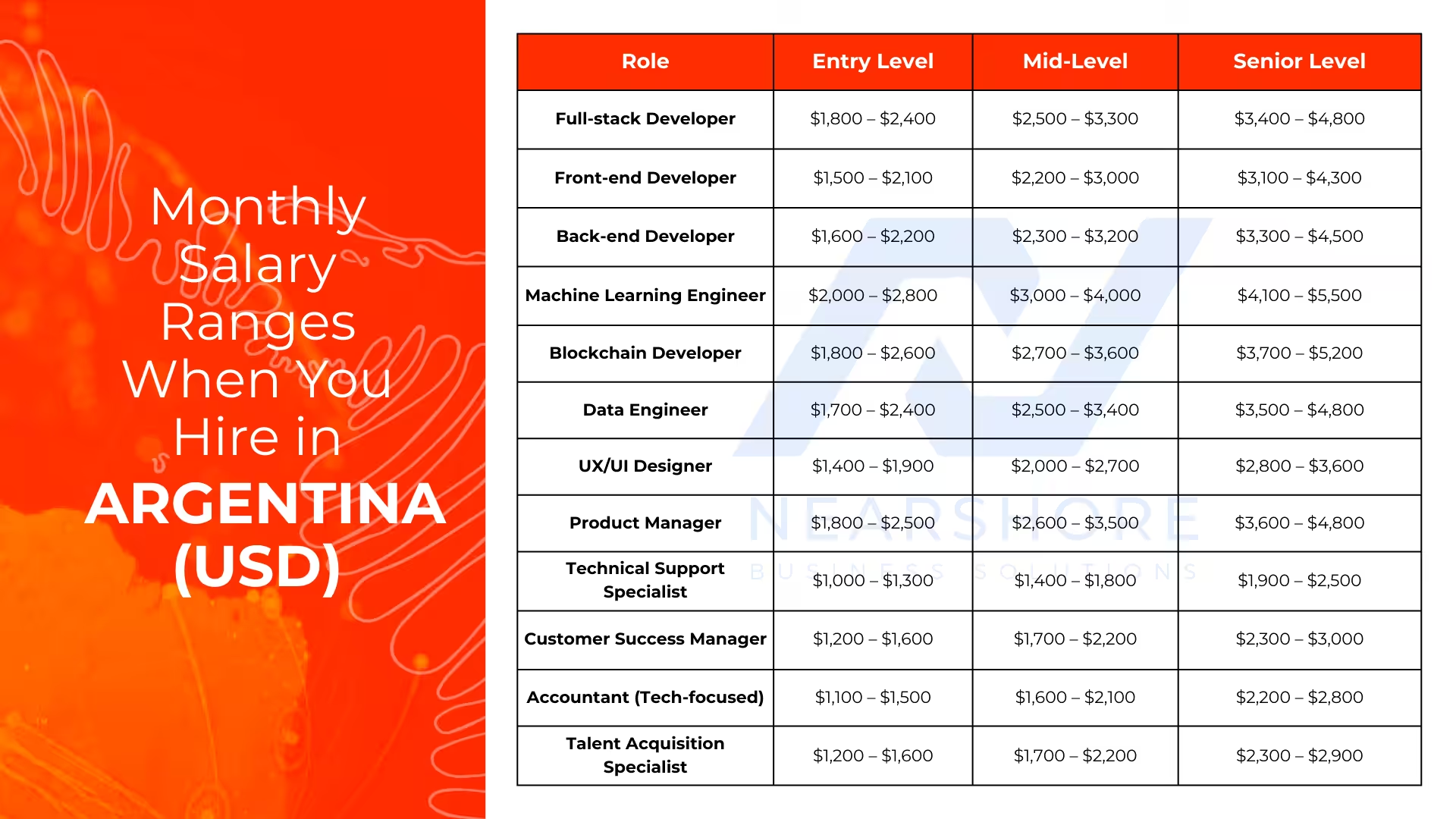
Monthly Salary Ranges in Argentina(USD)
These are average gross monthly salaries across entry, mid, and senior levels for common roles in Argentina. Actual compensation may vary based on location, experience, and language proficiency.
3 Legal Ways to Hire in Argentina
There are three main ways to hire and pay employees in Argentina, each offering different levels of control, compliance, and setup requirements. Understanding these options is crucial for businesses aiming to expand their operations into the Argentine market while ensuring adherence to local labor laws and regulations.
Establishing a legal business entity in Argentina is often necessary for hiring and paying remote workers, involving complexities such as opening a bank account for foreign payments and complying with local laws.
1. Independent Contractors
Independent contractors operate as self-employed professionals and manage their own taxes and benefits. This hiring model is particularly appealing for companies looking for flexibility and cost-effectiveness without the need to establish a local presence.
- Pros: Fast onboarding, low cost, no need for a local entity. Engaging independent contractors can significantly reduce administrative burdens and operational expenses, as businesses are not required to provide employee benefits or manage payroll taxes.
- Cons: Risk of misclassification, less oversight, no employee benefits. It’s essential to clearly define the scope of work and ensure that the contractor’s role does not resemble that of an employee to avoid potential legal issues related to worker misclassification.
When hiring a contractor in Argentina, it is crucial to understand the local labor laws, payment methods, and legal requirements to ensure compliance and smooth operations. Companies should also consider how to pay contractors, the implications of intellectual property protections, and confidentiality agreements to safeguard their business interests.
2. Employer of Record (EOR)
An EOR serves as the legal employer while the company manages daily activities. The EOR handles payroll, compliance, and benefits, making it easier to hire and pay remote workers in Argentina. This model allows businesses to quickly enter the Argentine market and hire local talent without the complexities of setting up a legal entity.
- Pros: Full legal compliance, fast market entry, no entity required. Using an EOR can streamline the hiring process, providing peace of mind regarding local compliance and enabling companies to focus on core business functions.
- Cons: Monthly service fees, less direct control over HR policies. While the EOR manages employment-related responsibilities, companies may have limited influence over specific HR practices and policies.
Additionally, hiring foreign employees through an EOR involves specific requirements and regulations, such as obtaining work visas and legal documentation, which vary based on the employee’s nationality, particularly for those from Mercosur countries versus non-member countries. This consideration is vital for maintaining compliance and ensuring a smooth onboarding process for international hires.
3. Local Entity Setup
Establishing your own local entity allows the company to hire employees directly and manage HR, payroll, and operations. This option is ideal for businesses planning long-term operations and significant investment in Argentina.
- Pros: Full control, strong brand presence, long-term scalability. Having a local entity provides the opportunity to build a robust organizational structure, align company culture, and establish a strong market presence.
- Cons: Higher cost and complexity, legal setup required, longer onboarding time. Setting up a local entity involves navigating complex legal and regulatory frameworks, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Creating a local entity involves several steps, including selecting the appropriate legal structure, registering with local authorities, and obtaining necessary licenses and permits. Businesses should also be prepared to comply with Argentine labor laws, including employment contracts, statutory benefits, and payroll contributions, to ensure legal and operational compliance.
Overall, choosing the right hiring model depends on the company’s strategic goals, budget, and operational needs. By carefully evaluating these options, businesses can effectively hire and manage employees in Argentina, leveraging the country’s skilled workforce and strategic advantages for growth and success.
Employment Compliance in Argentina
Hiring employees in Argentina requires full compliance with the country’s labor laws, which are protective of workers and highly regulated.

Employee Benefits and Rights
Employees in Argentina are entitled to a range of benefits and rights, including:
- Paid Sick Leave: Up to 3 months per year
- Maternity Leave: Up to 3 months per year
- Annual Leave: Up to 20 days per year
- Severance Pay: Up to 1 month’s salary per year of service
- Social Security Contributions: 23% of the employee’s salary
- Income Tax: 9% to 35% of the employee’s salary
- Statutory Benefits: Including life insurance and unemployment insurance
Employers must also comply with the labor laws and regulations, including the Labor Contract Law, and provide employees with a safe and healthy work environment. Employees are also entitled to join collective bargaining agreements and participate in union activities.
How to Set Up a Business in Argentina
Setting up a local entity allows companies to directly hire employees and operate long-term in Argentina. When deciding between utilizing an Employer of Record (EOR) and establishing a business entity, it’s important to consider that an EOR is faster to set up, while having a local business entity may offer better long-term cost-effectiveness and tailored compliance for companies planning to scale in the region.
Legal Structures
- Simplified Stock Company (S.A.S.): Most common for foreign businesses; can be formed by one shareholder. This structure offers flexibility and is designed to simplify the incorporation process, making it ideal for startups and small businesses looking to enter the Argentine market quickly.
- Limited Liability Company (SRL): Requires two or more partners; suitable for small to medium operations. This structure is favored for its straightforward management and limited liability protection, appealing to companies that want to share ownership and responsibilities among several partners.
- Corporation (S.A.): Requires at least two shareholders; suited for large-scale operations. Corporations are ideal for businesses planning significant investment and expansion, as they offer a robust framework for raising capital and managing complex operations.
Registration Steps
- Select and reserve company name: Ensure the chosen name is unique and complies with local regulations.
- Draft and notarize company bylaws: These documents outline the company’s governance structure and operational guidelines.
- Register with the Public Registry of Commerce: This step formally establishes the company as a legal entity in Argentina.
- Obtain a CUIT (tax ID) from AFIP: The CUIT is essential for tax purposes and must be acquired before commencing operations.
- Enroll in social security and tax systems: This enrollment is necessary to comply with Argentine labor laws and ensure proper employee benefits.
- Open a corporate bank account: A local bank account is required for financial transactions, including payroll and tax payments.
- Apply for a temporary residence visa: Foreign employees may need a temporary residence visa to live and work in Argentina legally.
Corporate Banking
- Required to process payroll, pay taxes, and operate locally. Efficient banking services are crucial for smooth business operations and financial management.
- Major banks include Banco Nación, Santander, BBVA, and HSBC. These banks offer a range of services tailored to meet the needs of foreign businesses operating in Argentina.
- Required documents: bylaws, CUIT, registration certificate, legal representative’s ID. Having these documents ready can expedite the account opening process and help avoid delays.
- Foreign employees must obtain a work visa to be legally employed in Argentina.
Establishing a business in Argentina requires careful planning and adherence to local regulations. By choosing the right legal structure and following the necessary registration steps, companies can effectively position themselves for success in the Argentine market. Additionally, leveraging local banking services ensures efficient financial management, which is crucial for long-term sustainability and growth.
Ongoing Compliance & Management
Once the business is operational, ongoing compliance is essential to remain in good standing with Argentine authorities.
Annual Tax and Reporting Obligations
- File annual corporate income tax returns to pay income tax
- Monthly/quarterly VAT and gross income tax filings
- Submit annual financial statements under IFRS
- Residents must report their worldwide income, while non-residents are taxed solely on income derived from Argentine sources
Payroll and Social Security
- Monthly payments to health, pension, and labor risk funds
- Accurate payroll processing with proper deductions and payslips
- Timely payments to avoid penalties
Risk Mitigation
- Maintain compliant contracts and HR policies
- Use legal advisors or accountants to manage updates in labor and tax laws
- Conduct regular audits to reduce the risk of fines or dispute
- Failure to comply with Argentine labor laws regarding worker classification may result in additional fines, emphasizing the importance of accurate classification to avoid legal and financial repercussions.
How to Legally Terminate an Employee in Argentina
Terminating employees in Argentina must follow strict legal procedures, including adhering to the required notice period, to avoid penalties and litigation.
Grounds and Procedures
- Just Cause: Must be supported by documentation (e.g., misconduct, repeated absenteeism, breach of contract)
- Without Cause: Permitted but requires full severance compensation
- Probationary Period: Up to 3 months; termination allowed with 15 days’ notice and no severance
Severance and Notice Periods
- Severance Pay: One month’s salary per year of service (or a fraction thereof)
- Unused Benefits: Must pay unused vacation, proportional 13th-month salary, and other accrued entitlements
- Notice Periods:
- 15 days if less than 5 years of service
- 30 days if more than 5 years of service
Employees with more than five years of continuous employment are also entitled to paid sick leave for up to six months.
Mutual Termination
- Requires a written agreement
- Should specify compensation and waive future claims
- Recommended to sign before a labor authority for legal protection
Key ConsiderationsAll terminations must be clearly documented and compliant with the LCT. Failure to follow due process may lead to reinstatement orders or fines.
Working Hours and LeaveEmployees are entitled to a standard workweek of 48 hours. Overtime pay is required for any hours worked beyond this, with employees receiving 50% extra for regular overtime and 100% extra for work during holidays or rest periods.
Conclusion
Argentina stands out as a strategic destination for hiring remote talent in Latin America. The country offers a large, educated workforce with strengths in software development, digital services, and professional operations—all at significantly lower costs than in the U.S. or Europe. Time zone overlap with North America, high English proficiency, and a strong remote work culture make Argentina ideal for global companies building distributed teams.
Foreign businesses have flexible hiring options in Argentina, including working with independent contractors, partnering with an Employer of Record (EOR), or establishing a legal entity for full control. Regardless of approach, understanding local labor laws, payroll obligations, and compliance requirements—particularly around worker classification and tax withholding—is essential for successful hiring in Argentina.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hiring in Argentina
1. What is the minimum wage in Argentina in 2026?
As of January 2026, the minimum wage is ARS 341,000 per month (approximately USD $234). The Argentine government has established a progressive schedule with monthly increases throughout 2026, reaching ARS 376,600 by August 2026. These rates are subject to periodic adjustment to account for inflation and cost of living changes. Employers must ensure compliance with these updates to maintain legal employment practices.
2. Can I hire talent in Argentina without opening a local entity?
Yes, using an Employer of Record (EOR) allows you to hire full-time employees without setting up a local business. This approach provides a streamlined entry into the Argentine market, enabling companies to manage employee payroll, benefits, and compliance efficiently while focusing on core business operations.
3. What are the most in-demand roles in Argentina?
Software developers, data engineers, product managers, digital marketers, and customer support specialists are highly sought after. The demand for these roles is driven by Argentina’s burgeoning tech sector and the increasing need for digital transformation across industries. Companies value Argentina’s skilled professionals for their technical expertise and adaptability in a rapidly changing global market.
4. What is the standard workweek in Argentina?
The legal maximum is 48 hours per week (8 hours per day), typically distributed Monday through Saturday noon. However, many modern employers, particularly in professional settings, adopt a 40-hour workweek. Overtime must not exceed 3 hours per day, 30 hours per month, or 200 hours per year. Overtime is compensated at 150% of regular pay for work Monday through Saturday before 1 PM, and 200% for work after 1 PM Saturday, Sundays, and public holidays.
5. What employer contributions are required in Argentina?
Employers must contribute approximately 24-26.4% of an employee’s gross salary to social security, covering:
- Pension fund: ~10.17%
- Healthcare: ~6%
- Other social services and family allowances: ~7-10%
- Labor risk insurance (ART): Varies by industry risk classification (typically 1-3%)
Note: Employers are exempt from contributing social security on the first ARS 7,003.68 of each employee’s monthly salary. These contributions are essential for providing employees with statutory benefits and ensuring compliance with Argentine labor laws.
6. How is severance calculated in Argentina?
For termination without just cause: One month’s salary per year of service (including any fraction greater than 3 months), plus accrued entitlements such as unused vacation days, proportional aguinaldo (13th-month salary), and notice period compensation. This calculation underscores the importance of fair employment practices and the need for employers to maintain proper documentation and understanding of local labor laws to handle terminations appropriately.
7. Is English widely spoken in the workforce?
Yes, particularly in tech, business, and customer-facing roles in major cities like Buenos Aires and Córdoba. English proficiency enhances Argentina’s appeal as a destination for international business, facilitating effective communication and collaboration with global teams. Many professionals in these sectors have strong English skills developed through education and international work experience.
8. What are the options for setting up a company in Argentina?
Common structures include:
- Simplified Stock Company (S.A.S.): Flexible, suitable for startups and small businesses
- Limited Liability Company (SRL): Popular for foreign investors
- Corporation (S.A.): Best for larger operations
Each structure offers different benefits and requirements regarding capital, governance, and liability, allowing businesses to choose the most suitable option based on their operational needs and long-term objectives.
9. How long does it take to set up an entity in Argentina?
Generally a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on documentation completeness and legal processing. The S.A.S. structure typically has the fastest setup time. Efficient planning and coordination with local legal experts can expedite this process, enabling businesses to establish a presence in Argentina and begin operations promptly.
10. Is Argentina a good choice for long-term remote team growth?
Yes. Argentina combines cost savings, talent availability, and favorable time zone alignment, making it ideal for scaling remote teams. The country’s investment in technology education, supportive government policies (such as the Knowledge Economy Law), and established remote work infrastructure further enhance its attractiveness as a hub for distributed teams and innovation.
How Can We Help You?
Whether you’re hiring your first role in Argentina or scaling an entire team, we support U.S. companies at every stage of the hiring journey:
- Remote Talent Recruitment – End-to-end recruiting for remote hires in Argentina, including market benchmarking, vetting, and candidate selection.
- In-Country Recruitment – Local, country-specific recruitment for companies building teams directly in Argentina.
- Recruitment as a Service (RaaS) – An embedded recruiting model where our team operates as an extension of yours to support ongoing or multi-role hiring needs.
- Staff Augmentation – Dedicated nearshore talent that integrates directly into your workflows, allowing you to scale teams quickly and predictably.
Ready to get started?
Tell us what roles you’re hiring for, and we’ll help you understand market availability, salary ranges, and the best hiring model for your team.
